1. Introduction
This document describes the data model that is defined by the Niord Nautical Information Directory project as of January 2017.
The actual source for the data model is available at the Niord Model Github Repository
2. Niord Message Model
The Niord Message Model is the combined model used to represent Navigational Warnings (NW) and Notices to Mariners (NM).
The model is used as an interchange format when communicating NW and NM messages with the Niord Editing System and compatible systems.
A public API for fetching Niord Message data from a test system can be found at the
Niord alpha server.
The API is documented in the Niord Public API document.
Please also find Guidelines as to how a client should render Niord model messages.
2.1. Background
The structured NW-NM data of the Niord Message Model needs to cater for the requirement set out by the specifications for MSI and NM T&P respectively, i.e. the relevant parts of:
-
Joint IHO-IMO-WMO S-53 standard on Maritime Safety Information.
-
IHO S-4 standard, which covers NM T&P.
-
Revised NAVTEX Manual MSC Circular.
-
IMO International SafetyNET manual.
The data model has been a further development of the work conducted in the EU-funded ACCSEAS project, documented in:
-
ACCSEAS WP6 MSI/NM (T&P) Service Description.
It has subsequently been updated according to the progress of the S-124 specification, an effort by IHO to create an S-100 specification for Navigational Warnings (and possibly Notices to Mariners T&P).
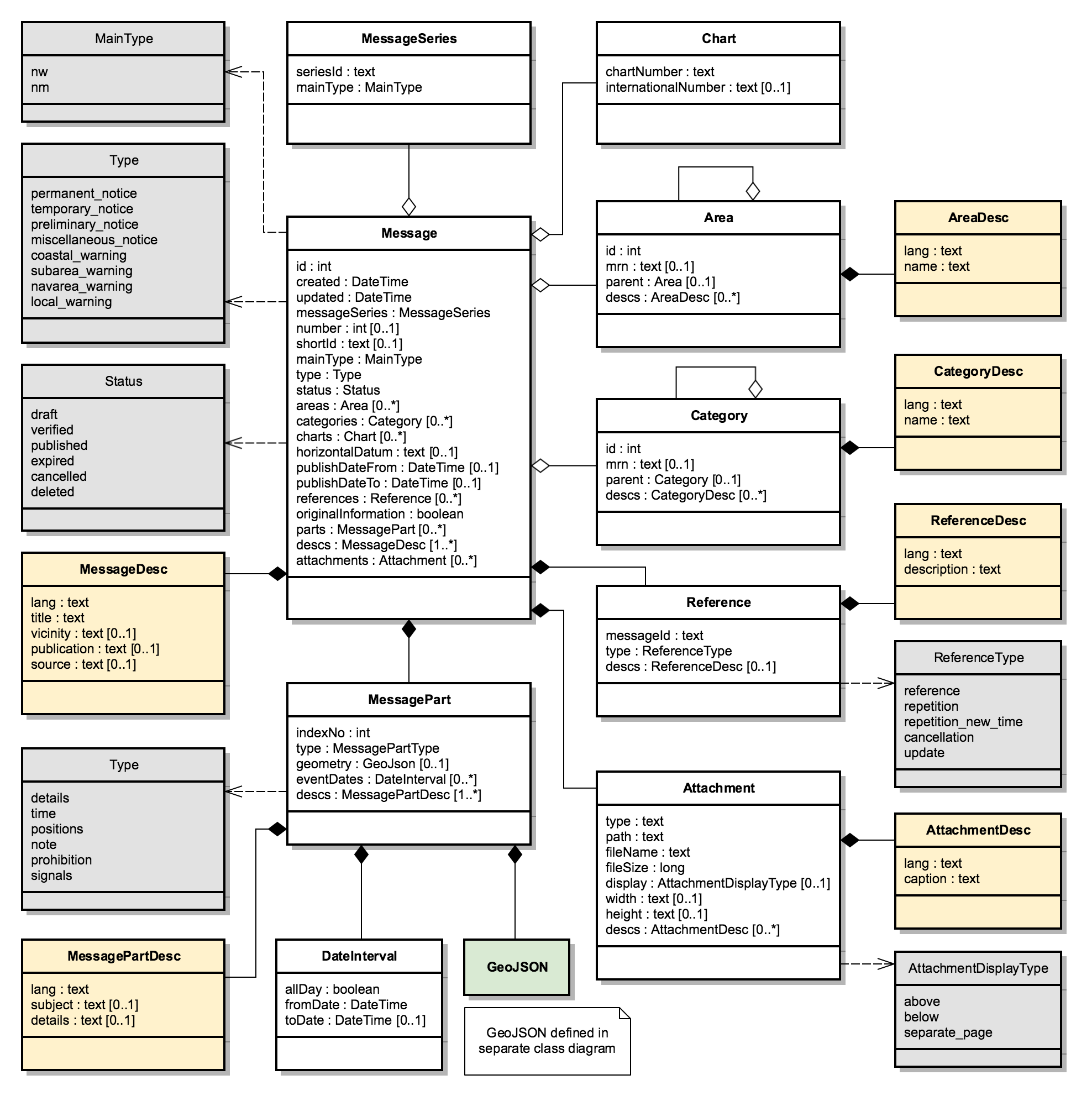
2.2. Message Model UML
The UML diagram for the message model is given by:
The diagram uses the following colour codes:
-
Light-gray background: Used for enumerations.
-
Light-yellow background: Used for localized description entities - see Design Pattern section below.
-
Light-green background: The GeoJSON model is detailed in the next chapter.
The use of aggregation vs composition connectors above is mostly academic, since the UML is not a database model but merely an interchange format. However, the aggregation connector is used to signal that the associated entity represents base data in the producing system, and is not tied to the life cycle of the Message.
2.3. Design Patterns
The overarching idea has been to generalize the constituent parts and fields of NW and NM T&P messages, and make the format both backwards compatible and future-proof by e.g. adding support for:
-
Multi-language support. All messages must be localizable to any number of languages, including the base data they reference (e.g. areas). The pattern adopted to support this, is to let all classes with localizable attributes (such as Message) have an associated list of description entities (MessageDesc) which contains an ISO 639-1 language code and the localizable fields. The description entities are yellow in the UML diagram below.
-
Rich text support. NM’s in particular, can contain a rich layout containing features such as tables, links, embedded pictograms, etc. By supporting HTML descriptions this can be accommodated.
-
New identifier format. The S-4 and S-53 standards loosely specifies a numbering scheme for NWs and NMs. However, the numbering scheme does not guarantee uniqueness in a combined NW-NM model, let alone a system that may contain messages from multiple authorities. Thus, the NW-NM data model introduces the generalized concept of message series used to group messages by.
-
Base data. Part of a combined NW-NM model is to define a relationship between messages and base data such as charts, categories and areas. Previous proposals have opted for rigid solutions with a fixed number of area and category levels, and with enumerated category values.
The remainder of the chapter will detail the individual classes.
2.4. Message Model Classes
The remainder of the chapter will detail the individual classes.
2.4.1. MessageSeries
According to IHO, NW and NM messages must be numbered. For NW, it is e.g. mandated that:
Navigational warnings in each series should be consecutively numbered throughout the calendar year, commencing with 1/YY at 0000 UTC on 1 January.
The numbering scheme does not guarantee uniqueness in a combined NW-NM model, let alone a system that may contain messages from multiple countries and authorities. Thus, message series have been introduced in the NW-NM data model to group messages as appropriate. A country may e.g. have separate message series for NW and NM. However, they may also introduce separate message series to allow, say, local harbour authorities to maintain their own message series for local NWs, or, as is the case with Canada, divide the country into five regions, each with their own message series.
| Attribute Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
seriesId |
String |
The ID of the message series in the implementing system. Should be globally unique. |
mainType |
MainType |
Either NW or NM. |
2.4.2. Chart
A message can be assigned a list of charts. The charts are maintained administratively as base data in the producing system.
| Attribute Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
chartNumber |
String |
Mandatory regional chart number (and identifier). |
internationalNumber |
String |
Optional international chart number. |
2.4.3. Area
Existing IHO standards for NW and NM both provide support for specifying multiple area levels (general area and locality for NW; general region, sub-region and specific location for NMs).
However, in the NW-NM system, this has been generalized, and areas are administratively maintained in a hierarchical area tree (with each area having a localized name) of arbitrary depth. A message can be assigned a list of these areas, and by implication, the parent areas of the selected area.
Additionally, a message can be assigned a localized textual vicinity description (part of the MessageDesc class), for detailed location information not defined in the area tree.
| Attribute Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
id |
Int |
Internal system ID of the area |
mrn |
String |
Optionally, an area may be assigned a globally unique MRN (maritime resource name). |
parent |
Area |
Non-root areas will reference their parent areas, and thus allow clients to e.g. group and sort
messages by areas |
descs |
AreaDesc[] |
The list of localizable attributes for an area. See AreaDesc |
| Whereas clients may use message areas for e.g. grouping or filtering messages, there is no reason to render the areas for the end user. The areas of a message will often be part of the message title already. |
2.4.4. AreaDesc
The AreaDesc class contains the list of localizable attributes for an area.
| Attribute Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
lang |
String |
The ISO 639-1 language code. |
name |
String |
The localized name of an area. |
2.4.5. Category
Categories are administratively maintained in a hierarchical category tree (with each category having a localized name) of arbitrary depth. A message can be assigned a list of these categories, and by implication, the parent categories of a selected category.
At the top level, the categories will have entries such as Aids to Navigation, Drifting Objects, Obstruction, etc., which is the categorization used in the IHO standards. The sub-categories will represent the types of hazard relevant to the parent category. Examples of category lineages (top-down):
-
AtoN → Floating AtoN → Buoy → Buoy Established
-
AtoN → Light → Light Unlit
-
Obstruction → Diving Operation
| Attribute Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
id |
Int |
Internal system ID of the category |
mrn |
String |
Optionally, a category may be assigned a globally unique MRN (maritime resource name). Adopting MRNs for categories would make interchange of message data between two NW-NM systems more robust. |
parent |
Category |
Non-root category will reference their parent categories. |
descs |
CategoryDesc[] |
The list of localizable attributes for a category. See CategoryDesc. |
| The main purpose of categories is to allow for client filter and customized portrayal. There is no reason to render the categories separately for the end user. |
2.4.6. CategoryDesc
The CategoryDesc class contains the list of localizable attributes for a category.
| Attribute Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
lang |
String |
The ISO 639-1 language code. |
name |
String |
The localized name of a category. |
2.4.7. Reference
The Reference class provides a typed, weak reference to another message.
| Attribute Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
messageId |
String |
An identifier of the referenced message. If the messageId is recognized to be a short-ID of another message, it can e.g. be used to hyperlink to that message. However there are no requirements as to the format of the message ID. |
type |
ReferenceType |
The type of the reference. One of the values "reference", "repetition", "repetition_new_time", "cancellation" or "update". |
descs |
ReferenceDesc[] |
The list of localizable attributes for a Reference. See ReferenceDesc. |
2.4.8. ReferenceDesc
The ReferenceDesc class contains the list of localizable attributes for a reference.
| Attribute Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
lang |
String |
The ISO 639-1 language code. |
description |
String |
The localized description of a reference. |
2.4.9. Attachment
Messages can be associated with a list of attachments, such as images, PDF-files, etc. The physical attachment files will reside in a public repository on the producing system.
| Attribute Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
type |
String |
The content type of the attachment file, such as "image/png". |
path |
String |
The URL path to the attachment file in the producing system. |
fileName |
String |
The file name of the attachment |
fileSize |
Long |
The size of the attachment in bytes |
display |
AttachmentDisplayType |
If defined, this flag can be used to signal how the editor intended for the (image or video) attachment to be displayed when rendering the message for the end user. "above" and "below" signals that the attachment should be displayed above, respectively below, the message details. "separate_page" signals that the attachment should be displayed on a separate page if rendered in paged media, such as a PDF file. |
width |
String |
The width to use when displaying the (image or video) attachment. The width must include the type (i.e. em, px, %, cm, mm, in, pt or pc). If the height attribute is left unspecified, the attachment should be scaled proportionally. |
height |
String |
The height to use when displaying the (image or video) attachment. The height must include the type (i.e. em, px, %, cm, mm, in, pt or pc). If the width attribute is left unspecified, the attachment should be scaled proportionally. |
descs |
AttachmentDesc[] |
The list of localizable attributes for an Attachment. See AttachmentDesc. |
| If the client wish to work in offline mode, it should download all attachments locally, and rewrite attachment paths accordingly. Also, since attachments may be embedded as images or links in the HTML of the message part details field (see MessagePartDesc), this field should be rewritten as well. |
2.4.10. AttachmentDesc
The AttachmentDesc class contains the list of localizable attributes for an attachment.
| Attribute Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
lang |
String |
The ISO 639-1 language code. |
caption |
String |
A localized caption to display for the attachment. |
2.4.11. DateInterval
A message part will have an associated list of (possibly open-ended) event date intervals. This defines the period of time for which the hazard described by the message part applies.
| Attribute Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
allDay |
Boolean |
If the allDay flag is set, the fromDate/toDate attributes should be treated as dates without a time-part by the producing system. |
fromDate |
DateTime |
The start date-time of a date interval. |
toDate |
DateTime |
An optional end date-time of a date interval. |
| Clients may use event dates for filtering messages (e.g. filter for relevance in route planning). However, the client should not render the event dates for the end user, since a textual representation of the dates should be included in the message part details (see MessagePartDesc). |
2.4.12. MessagePart
A message defines an ordered list of message parts, which can be thought of as sub-stories. Conceptually, each message part defines the time, positions, key subject and description of the hazard or event that the story pertains to.
| Attribute Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
indexNo |
Int |
Specified the ascending index of the message part within the message |
type |
MessagePartType |
May be used by the client to tag the message tag details with a type. Valid types are "details", "time", "positions", "note", "prohibition" and "signals". |
geometry |
GeoJSON |
The positions of the message part. The GeoJSON type is treated in details in the Niord GeoJSON Model chapter. In practice, Niord will always return a FeatureCollection GeoJSON entity. |
eventDates |
DateTime[] |
The list of event dates for which the message part hazard pertains. The list should not be rendered for the end user by the client, but may be used for computations. |
descs |
MessagePartDesc[] |
The list of localizable attributes for a MessagePart. See MessagePartDesc. |
2.4.13. MessagePartDesc
The MessagePartDesc class contains the list of localizable attributes for a message part.
| Attribute Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
lang |
String |
The ISO 639-1 language code. |
subject |
String |
The key subject of the hazard or event that the message part pertains to. |
details |
String |
A detailed description of the hazard or event that the message part pertains to. The type of the details field is mandated to be HTML, and thus allows for fairly advanced layout and typography, and may contain elements such as tables, links, images, etc. |
2.4.14. Message
The Message class represents a complete Navigational Warning (NW) or Notices to Mariners (NM) nautical information message.
It has been a deliberate choice to let NWs and NMs share the same Message class, rather than having a separate sub-class for each type. The main rationale for this is that NWs and NMs T&P are expected to converge in the future, once promulgation is handled completely via electronic means.
| Attribute Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
id |
Int |
Internal system ID of the message |
created |
DateTime |
The timestamp the message was created in the system. |
updated |
DateTime |
The timestamp the message was last updated in the system. |
messageSeries |
MessageSeries |
The message series of the message. See MessageSeries section. |
number |
Int |
The sequence number of a published message. See MessageSeries section. |
shortId |
String |
The short-ID of a published message. See MessageSeries section. |
mainType |
MainType |
The main type of the message, either NW or NM. In reality this attribute is redundant, since the main type is also defined by the associated message series, and may be implied by the message type. It is included for convenience. |
type |
Type |
The sub-type of the message. One of "permanent_notice", "temporary_notice", "preliminary_notice", "miscellaneous_notice", "coastal_warning", "subarea_warning", "navarea_warning" or "local_warning". |
status |
Status |
The status of the message. One of "draft", "verified", "published", "expired", "cancelled" or "deleted". |
areas |
Area[] |
A list of the areas of a message. See Area section. |
categories |
Category[] |
A list of the categories of a message. See Category section. |
charts |
Chart[] |
A list of the charts of a message. See Chart section. |
horizontalDatum |
String |
The horizontal datum for the message. If unspecified, assume WGS-84. |
publishDateFrom |
DateTime |
The timestamp for when the message was published – or should be published. |
publishDateTo |
DateTime |
The timestamp for when the message was cancelled – or should be expired. |
references |
Reference[] |
A list of message references. See Reference section. |
originalInformation |
Boolean |
If the message is based on original information or not. |
parts |
MessagePart[] |
The list of message parts of the message. See MessagePart section. |
descs |
MessageDesc[] |
The list of localizable attributes for a Message. See MessageDesc section. |
attachments |
Attachment[] |
The list of message attachments of the message. See Attachment section. |
2.4.15. MessageDesc
The MessageDesc class contains the list of localizable attributes for a message.
| Attribute Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
lang |
String |
The ISO 639-1 language code. |
title |
String |
A complete title line to show for a message. Typically composed by concatenating the area lineage, vicinity and subject of each message part. Example: "Denmark. The North Sea. Hanstholm SW. AIS buoyage established." |
vicinity |
String |
May be used for localized arbitrary area information not defined in the area tree. See Area section. |
publication |
String |
A textual listing of all the publications relevant to the message. The format of the publication field is mandated to be HTML, as it may contain links to the actual publications. |
source |
String |
A textual listing of all the sources and dates of the message hazard information. |
3. Niord GeoJSON Model
The Niord GeoJSON Model is an implementation of an external data model, as defined at GeoJSON Specification.
GeoJSON was picked as the representation of a message geometry, because it is widely adopted by client libraries, and, unlike e.g. WKT, the GeoJSON Feature class has associated properties that can be used to store various information, that may be used in the portrayal of the messages.
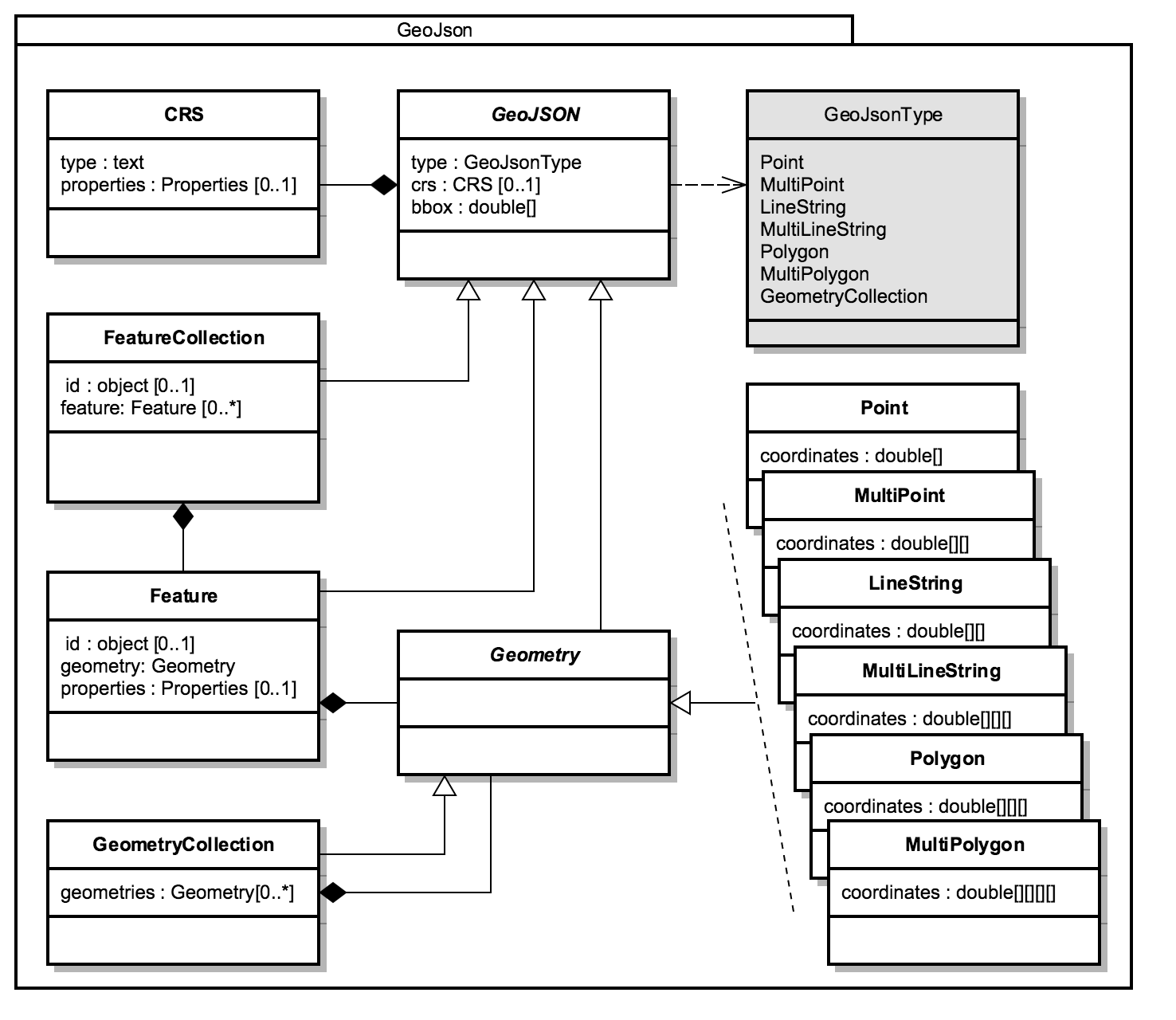
3.1. GeoJSON Model UML
The UML diagram for the GeoJSON model is given by:
The classes will not be detailed in this chapter, since the documentation can be found at the GeoJSON Specification page.
3.2. Niord GeoJSON Extensions
A client should be able to display the GeoJSON-based geometry data associated with each message (actually, each message part of each message).
On top of the GeoJSON standard, Niord has defined a set of GeoJSON Feature properties that a client
may optionally support, in order to improve the portrayal and user experience.
The custom feature properties may e.g. enrich the geometry with feature and coordinate labels and restriction flags.
| Property Name | Description |
|---|---|
name:lang |
Contains a language-specific name that can be displayed for the geometry of the entire Feature. Example: name:en = Area of reduced depth. |
name:x:lang |
Contains a language-specific name that can be displayed for the x’th coordinate of the geometry of the Feature. Example: name:12:en = yellow spar buoy with topmark. |
restriction |
The restriction flag may be used to adjust portrayal of a GeoJSON Feature, and whether or not to include the message in, say, route planning. Valid restriction values are "affected", "restricted", "speed-restricted", "prohibited" and "stopping-prohibited". |
parentFeatureId |
These properties are mostly used by the producing system to let one geometry be defined from another geometry. As an example, an affected area may be defined as a buffered geometry with a radius of 200 meters around, say, the position of a wreck (this being the parent geometry). |